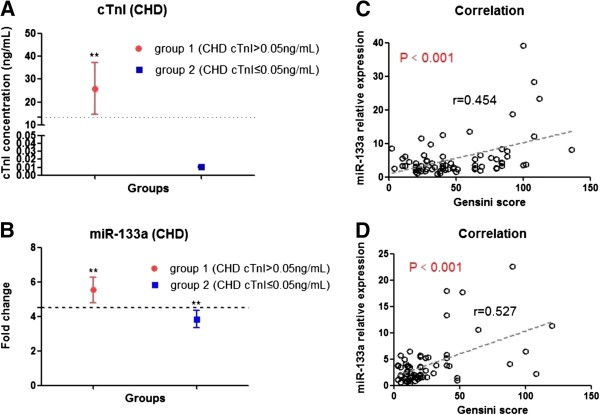
Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis | Journal of Translational Medicine | Full Text

Plasma Circulating Extracellular RNAs in Left Ventricular Remodeling Post-Myocardial Infarction - eBioMedicine

Increased MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133a Levels in Serum of Patients With Cardiovascular Disease Indicate Myocardial Damage | Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics
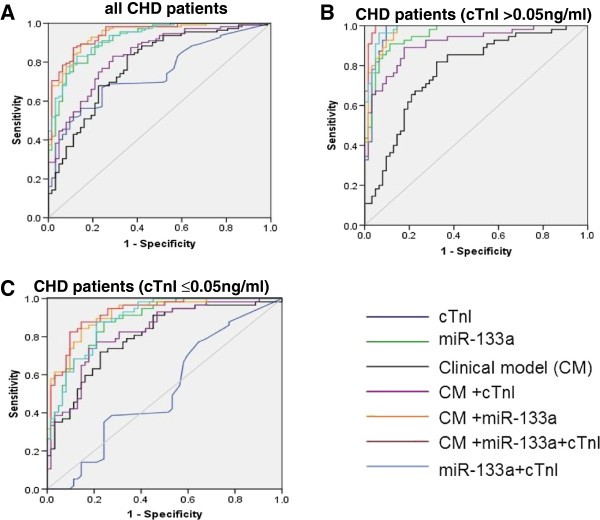
Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis | Journal of Translational Medicine | Full Text
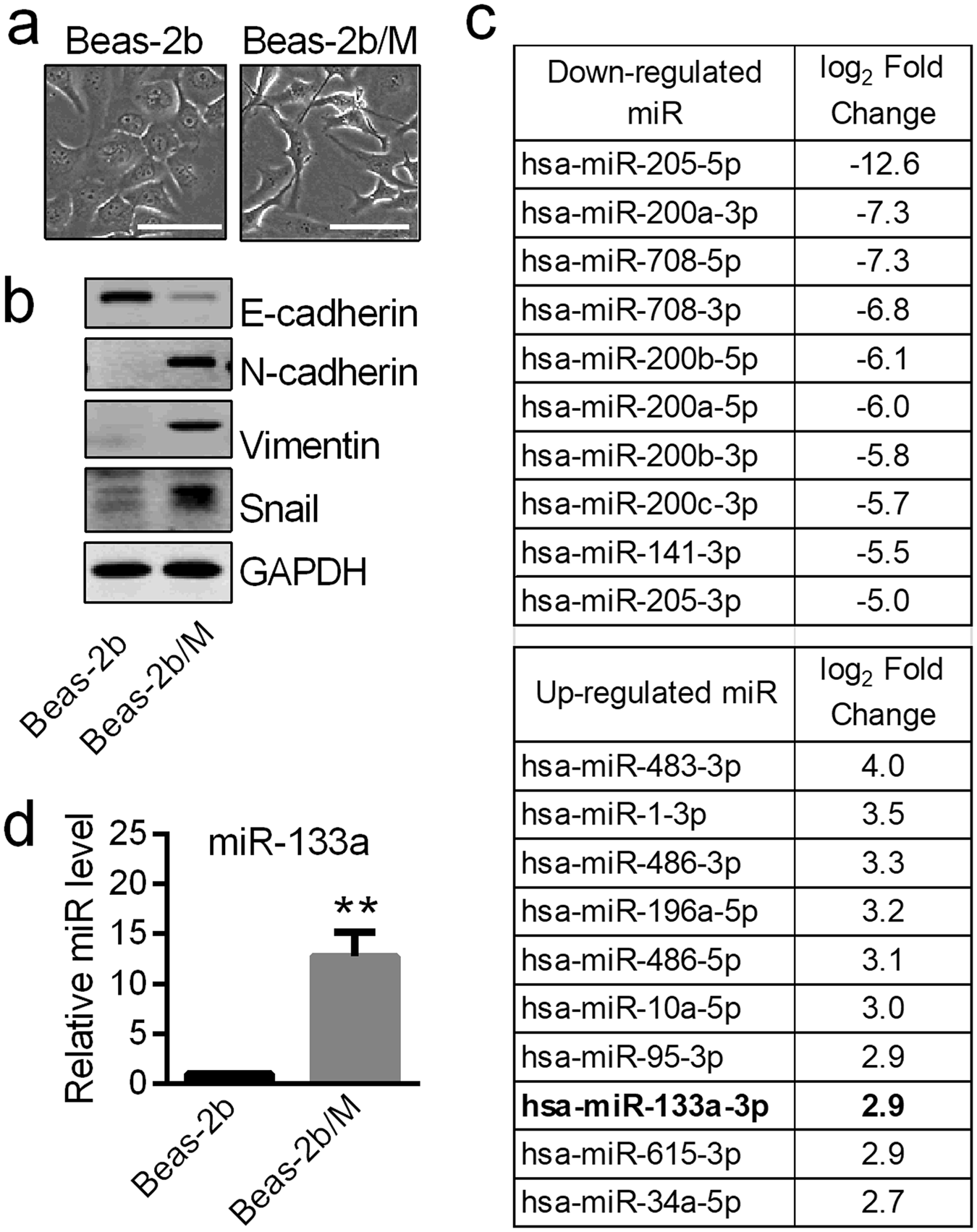
Up-regulated miR-133a orchestrates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of airway epithelial cells | Scientific Reports
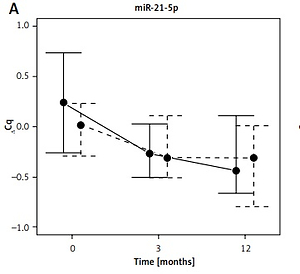
Twelve-month kinetics of circulating fibrosis-linked microRNAs (miR-21, miR-29, miR-30, and miR-133a) and the relationship with extracellular matrix fibrosis in dilated cardiomyopathy

MicroRNAs and Myocardial Infarct: Investigating the Controversial Role of Second Generation Biomarkers. | Semantic Scholar

miR-223-3p and miR-24-3p as novel serum-based biomarkers for myotonic dystrophy type 1: Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development
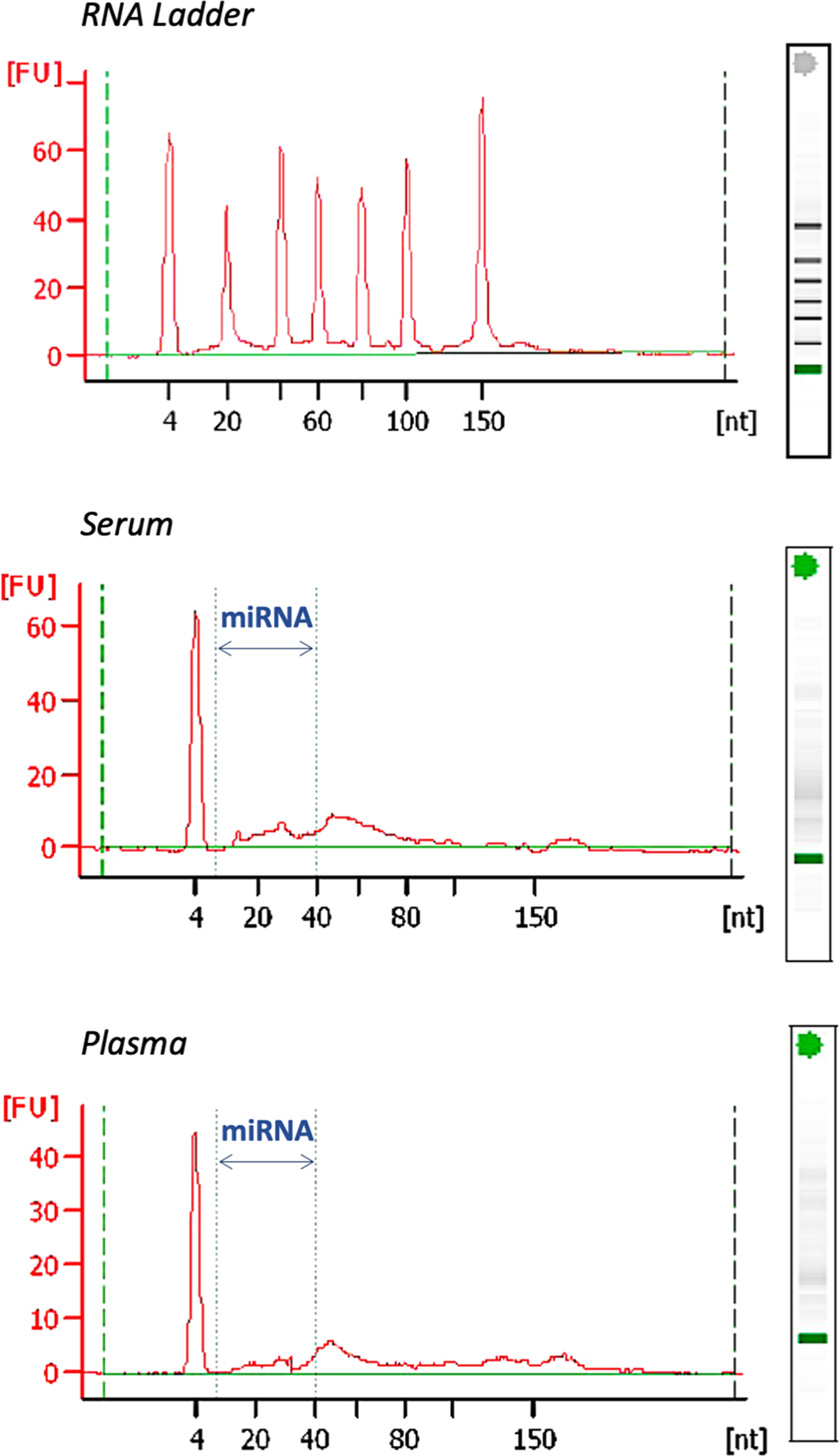
Disparate miRNA expression in serum and plasma of patients with acute myocardial infarction: a systematic and paired comparative analysis | Scientific Reports

MicroRNA plasma expression over time. A miR-1, B miR-133a, C miR-30a, D... | Download Scientific Diagram
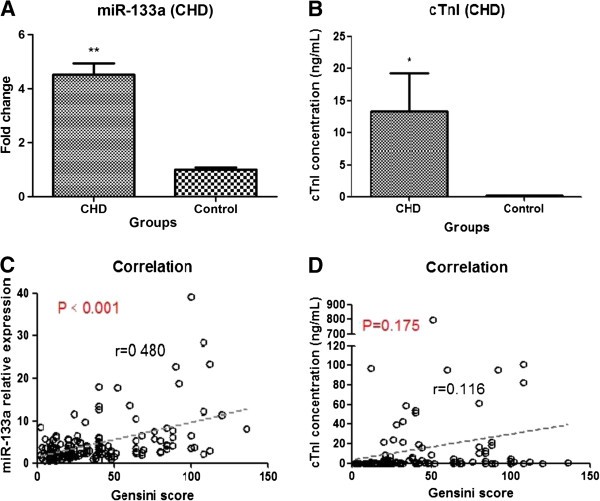
Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis | Journal of Translational Medicine | Full Text

microRNA‐based diagnostic and therapeutic applications in cancer medicine - Sempere - 2021 - WIREs RNA - Wiley Online Library

Systematic review and network analysis of microRNAs involved in cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and infarction: Involvement of redox signalling - ScienceDirect
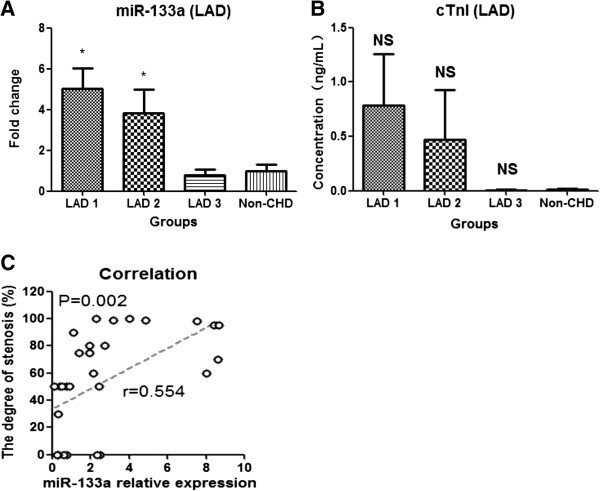
Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis | Journal of Translational Medicine | Full Text

Increased MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133a Levels in Serum of Patients With Cardiovascular Disease Indicate Myocardial Damage | Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics
Identification of cardiac-related circulating microRNA profile in human chronic heart failure | Oncotarget

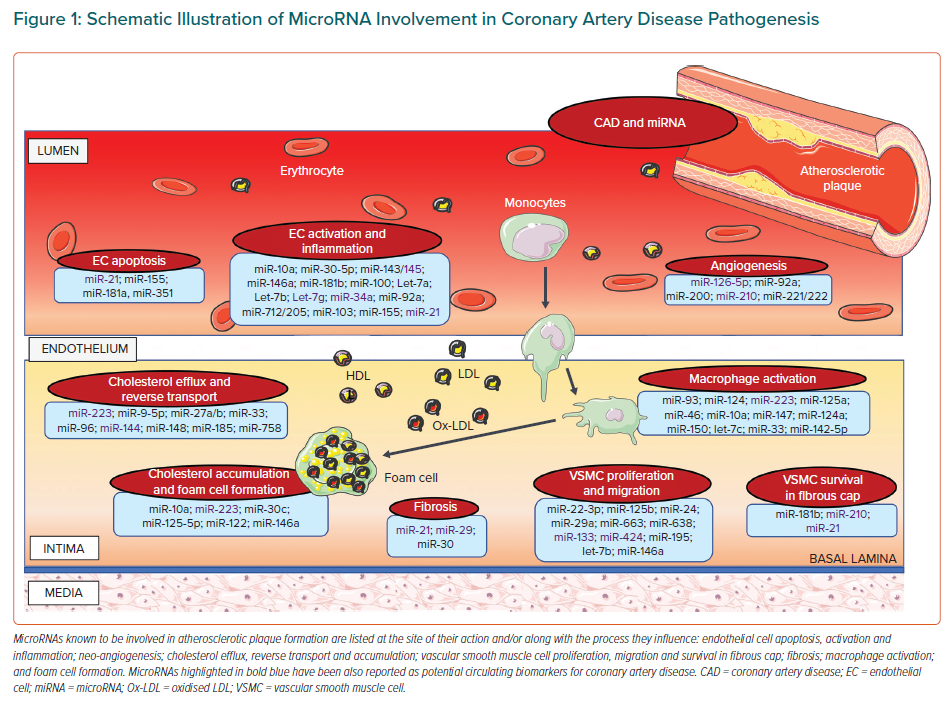
Circulating MicroRNAs: Potential and Emerging Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
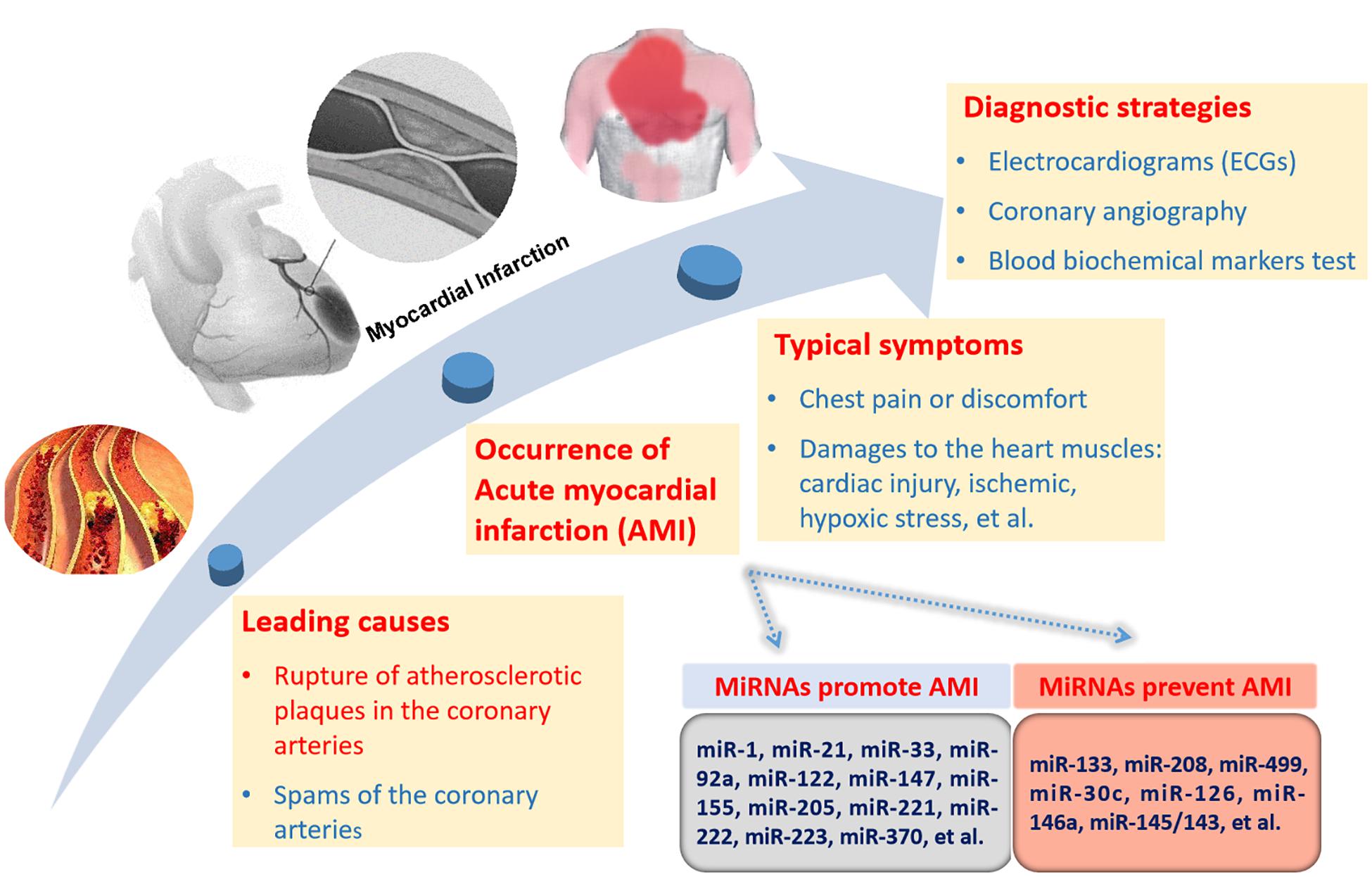
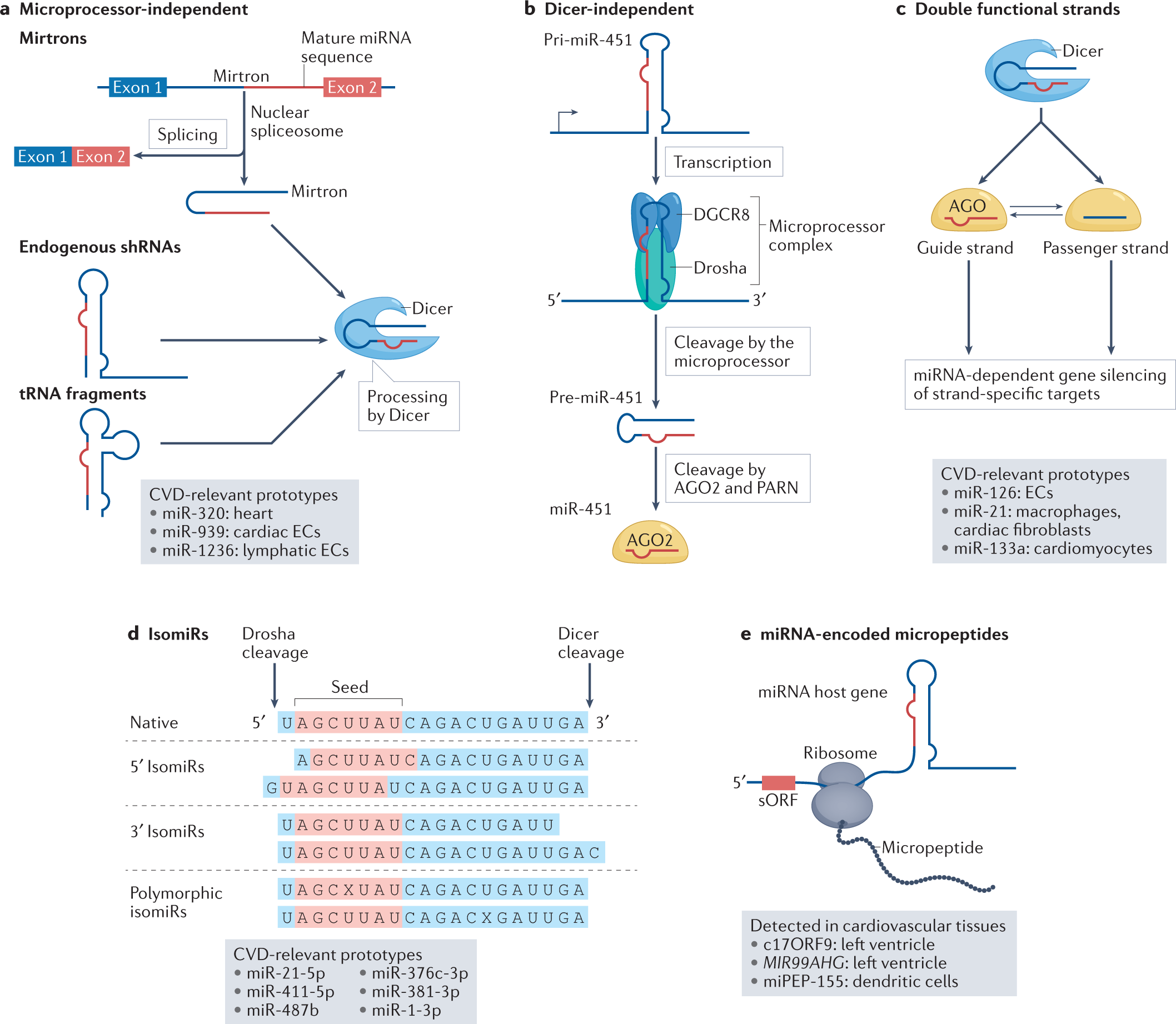
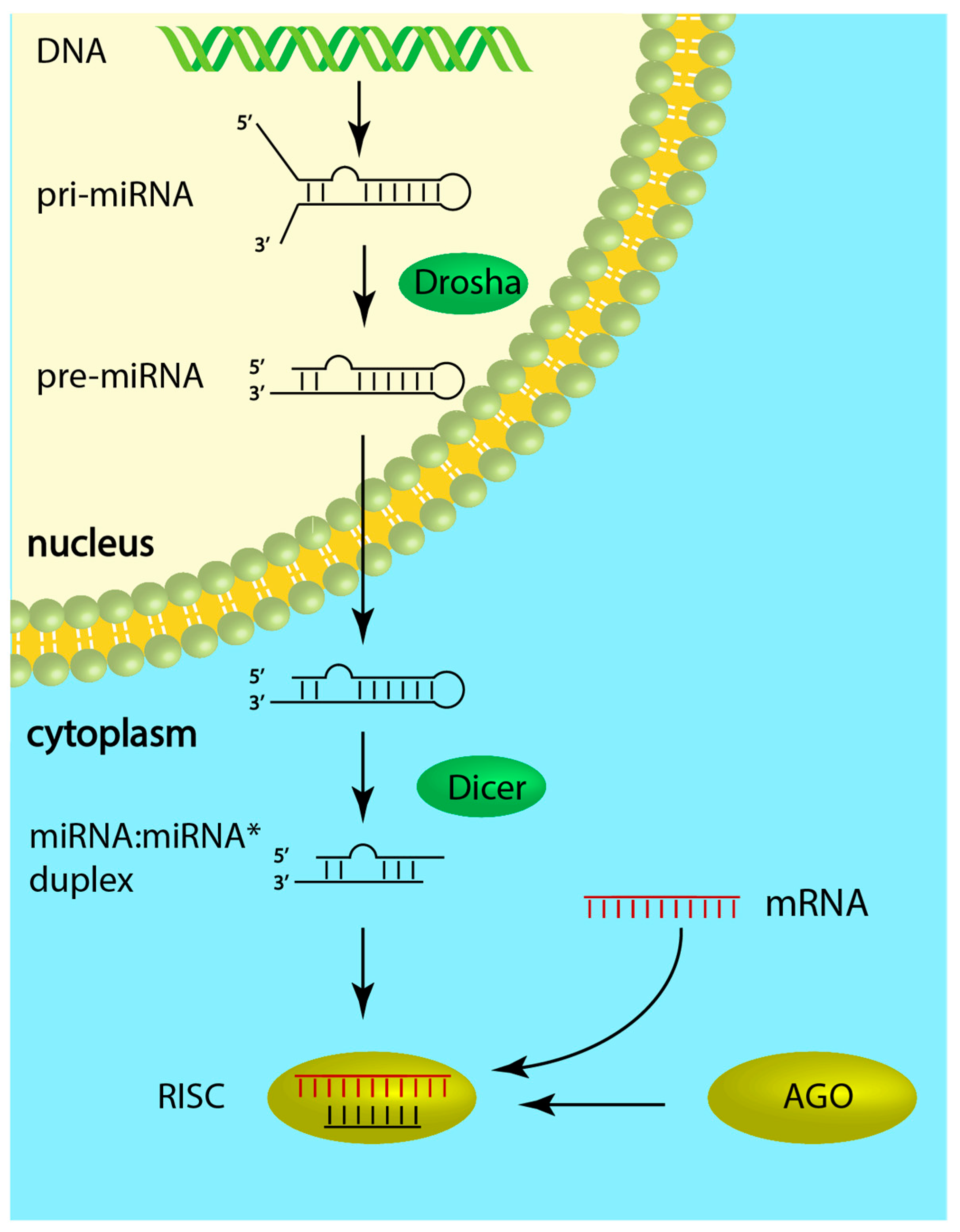
Frontiers | Circulating MicroRNAs: Biogenesis and Clinical Significance in Acute Myocardial Infarction

Increased MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133a Levels in Serum of Patients With Cardiovascular Disease Indicate Myocardial Damage | Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics